Trading Strategies in Volatile Markets: A Beginner’s Guide
If you’ve ever been caught in a sudden thunderstorm, you’ll understand that it can be both thrilling and daunting. Similarly, trading in volatile markets feels like navigating through choppy seas. Volatility can be your best friend or worst enemy, depending on how well-prepared you are. However, equipped with deep knowledge, dynamic risk management strategy, and the right map and compass (read: strategy), you may not only weather the storm but even harness its energy. Ready to dive in? Let’s set sail to understand trading strategies in volatile markets!
What is Volatility?
Think of volatility as the financial market’s version of a rollercoaster ride. It represents the frequency and intensity of price fluctuations in the market. Imagine a calm sea, where waves gently ebb and flow, versus a tempestuous one with towering waves crashing down. In market terms, a calm sea signifies low volatility, while the latter scene depicts a volatile market.
Why is Volatility important?
Why should a trader care about these ups and downs? Just as surfers are always on the lookout for the perfect wave, traders, especially those involved in volatility trading, seek opportunities in these price swings. Volatility can mean more potential opportunities, but it also comes with higher risk. Thus, understanding volatility is crucial for risk management and making informed trading decisions and trading strategies in volatile markets.
How to measure Volatility?
As the saying goes, “If you can’t measure it, you can’t improve it.” There are several tools to gauge market volatility, with a popular one being the Volatility Index (VIX). It’s like the market’s magic 8-ball, which can give traders indications of expected market fluctuations.
Is a Volatile Market good for trading?
Here’s where opinions diverge. Some traders may see potential in calm waters, while others can’t resist the adrenaline rush of trading in volatile markets. The latter believe that with greater risks come great rewards. A volatile market can offer more potential opportunities for traders who know how to leverage these conditions. But remember, where there’s potential for higher profit, there’s also a higher potential for significant loss.
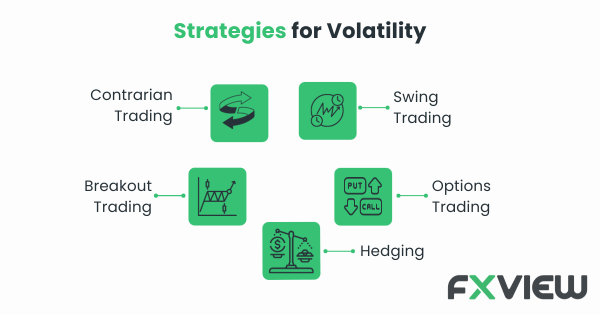
Trading strategies in Volatile Markets
Hold onto your hats; this is where things get spicy! Crafting trading strategies in volatile markets can be like creating a secret recipe. Let’s stir the pot with some examples of trading strategies in volatile markets!
Contrarian Trading
Definition: This strategy is based on the principle that when the majority of traders lean in one direction, the odds may favor a possible reversal.
Application: A contrarian trader may observe popular market sentiments and deliberately choose to go against the grain. If everyone is potentially bullish, they’ll look for selling opportunities and vice versa.
Example: In a hypothetical situation, if most retail traders are buying up shares of Company A due to positive news, the contrarian might decide to sell or short-sell those shares, anticipating an eventual price drop when the hype fades.
Swing Trading
Definition: This intermediate-term strategy focuses on capturing the ‘swing’ or change in momentum of a stock or asset over several days to weeks.
Application: Swing traders often use technical analysis to look for price patterns and key levels to enter and exit trades. This strategy can be especially useful during volatile markets where these swings are more pronounced.
Example: Imagine the stock of Company B fluctuates regularly between $10 and $15. A swing trader will aim to buy at or near $10 and sell at or near $15, catching the price “swing.”
Breakout Trading
Definition: Breakout trading involves entering a position as early as possible within a new price trend, usually after the asset breaks past a certain level of resistance or support.
Application: Traders identify key resistance and support levels. When the price of an asset breaks through these levels on high volume, it can indicate the start of a potential new trend in the direction of the breakout.
Example: If Company C’s stock price has struggled to surpass $20 several times but then suddenly breaks through to $21 on strong volume, a breakout trader might take a long position, anticipating further upward movement.
Hedging
Definition: This strategy involves taking an opposite position in a related security to offset potential losses in a primary investment.
Application: Commonly used in forex and commodities markets, hedging might involve trading derivatives or other instruments to balance the portfolio.
Example: An investor who owns physical gold might short gold futures. If the gold price falls, the losses on the physical gold could be offset by profits from the short position on gold futures.
Using Options
Definition: Options are financial derivatives that may give traders the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell an asset at a specific price on or before a particular date.
Application: During volatility, traders can use options strategies like straddles or strangles, which can allow them to take advantage of large price swings in either direction.
Example: If a trader expects Company D’s stock to move significantly after an upcoming announcement but isn’t sure of the direction, they might use a straddle by buying both a call and a put option at the same strike price and expiration. If the stock moves sharply in any direction, one of the options may become valuable enough to cover the cost of both options and yield potential.
Trading strategies in volatile markets offer a wide array of approaches, including contrarian trading, swing trading, breakout trading, hedging, and options trading. Adapting these strategies to the ever-changing market conditions requires skill and flexibility, making volatility a thrilling but challenging arena for traders.
Key Takeaways
Ride the Wave: Volatile markets are like tempestuous seas, with potential opportunities for those ready to ride the waves. Evaluating your risk tolerance and constructing a dynamic risk management plan is essential to forming effective trading strategies in volatile markets.
Know Your Tools: From the VIX to technical indicators, arm yourself with the right tools to measure and navigate through volatility.
Strategize, Don’t Gamble: Dive into volatility trading with a robust strategy, be it contrarian trading, swing trading, or hedging. Adjust and adapt as the market conditions shift.
Stay Informed: The sea of trading is ever-evolving. Continuous learning, staying updated with market news, and re-evaluating your trading strategies in volatile markets can be the wind beneath your trading sails.
Conclusion
As you sail through the choppy waters of trading in volatile markets, remember every seasoned sailor was once a beginner who dared to venture out into the deep. Understanding trading strategies in volatile markets and being able to manage your risks through the market’s ups and downs is important. With patience, practice, a well-charted course, and a dynamic risk management plan you may take advantage of the market opportunities, always taking into consideration your risk tolerance. Skillful trading, and may the winds of fortune always be with you!
Disclaimer: The information contained in this article is provided for educational and informational purposes only and it is not intended to be, nor does it constitute financial, investment or trading advice. You should not make any financial, investment or trading decision based on the information provided in this article without performing your own research or seeking advice from an independent advisor.
